Acabamos de montarnos en el autobús.
Después de comer hemos tenido juegos deportivos, algo de lluvia y tras la despedida nos hemos subido al autocar. Esperamos llegar en 20 minutos.
Todo bien salvo un mínimo incidente-lesión del fútbol.
Pero sobrevivirá...
Wednesday, 15 June 2016
EN RUTA
BUENOS DÍAS
Estamos llegando al final! 😥
Nos hemos levantado con alguna afonía más, hemos hecho las maletas y a desayunar, lo mismo que todos los días, leche, zumo, bizcochos, galletas, magdalenas y cereales.
Después estamos haciendo juegos en las pistas deportivas y en un rato iremos a la piscina.
A nivel organizativo, os comento, la salida está prevista a las 16:00, con lo que esperamos llegar al cole sobre las 16:30. De todos modos volveré a escribir e incluso el blog cuando estemos subidos en el autocar, para ajustar mejor los tiempos.
Buen día a tod@s
Tuesday, 14 June 2016
ÚLTIMA NOCHE
Bueno, llegamos a la última noche, que corto, ¿no?
Os cuento cómo vamos.
Después de comer, campeonato de ping-pong, con podium y todo. Lo pasamos bien. Después piscina, aunque se nos nubló, pero no había quien nos sacara del agua.
Hemos merendado, ¿os dije ayer que merendamos?, y hemos hecho juegos hasta la hora de la ducha.
Han salido guapetones esperando la disco de la noche. Alguna trajo pintalabios y ha compartido, así que muy guapas ellas también.
La cena de hoy estaba muy rica, ya os contarán (olvidé hacer la foto): guisantes con jamón, empanadillas, rabas y yogur.
Y ahora están todos con los teléfonos hablando con vosotros, algunos afónicos, veremos como llegan a mañana...
Vamos a disfrutar bailando y cantando.
Y YA HEMOS COMIDO
Bueno, ¡esto va muy rápido!
En estos momentos terminamos de comer.
Ya, los dos grupos han hecho tiro con arco y el taller de relojes de sol.
Ya os contaré que tal nos va la tarde...
BUENOS DÍAS
Buenos días a todos!
Después de una buena noche, nos hemos levantado, nos hemos aseado y hemos desayunado. Algunos tenemos cara de sueño todavía pero ya estamos en marcha.
Empezamos un grupo con tiro con arco y el otro con taller, ya os contaremos lo que hemos hecho.
Lo estamos pasando genial...
NOCHE
Por fin llegó la hora.
Después de las actividades de la tarde, se han aseado, han cenado, han tenido un rato de juego libre y después gymkhana nocturna.
Ahora ya están cada uno en su cabaña preparados para dormir...
Buenas noches
Monday, 13 June 2016
MAÑANA Y MEDIA TARDE
Buenas!
Después de acomodarnos en las cabañas hemos empezado las actividades.
Nos han dividido en dos grupos, que somos muchos, unos hemos ido al rocódromo y otros a multiaventura.
Por la tarde haremos lo contrario.
Después, a eso de la una, hemos ido a comer, un rato de juegos y piscina.
Estamos merendando ya y en breve nos vamos a las actividades de la tarde.
Os dejo una foto del menú y otra de la piscina, para que veáis qué mal lo pasamos...
YA HEMOS LLEGADO!
Después de un pequeño atasco, el conductor se las ha apañado para traernos dando un rodeo, así que ya hemos llegado.
Ya les están instalando en las cabañas.
Seguiremos informando!
Wednesday, 25 May 2016
WHAT ARE THE BENEFITS AND RISKS OF USING THE INTERNET?
We have instant access to information.
We can go shopping without leaving home.
It's easy to contact friends and family all around the world.
Risks:
Viruses can damage computers.
Criminals can access and steal information, products and money.
Long periods of computer use can cause health problems.
People sometimes use the Internet to bully other people.
The information on the Internet isn't always accurate.
WHAT'S WORD PROCESSING?
HOW TO EDIT TEXT IN WORD:
Checking spelling: Words that are spelt incorrectly are underlined in red.
Bold, underline and italics: Highlight the word with the mouse and then click on the bold or italics or underline button in the toolbar.
Creating lists: Highlight the list with your mouse, and then click on the number or bullet point icon in the toolbar.
Cut, copy and paste: To move text, highlight the text with the mouse. Click on the scissors icon to cut it. Then click on the place you want to move it to. Finally, click on the clipboard icon to paste it.
Saving and printing: It's important to save your work regularly. To save a document click on the disc icon in the toolbar. To print it, click on the printer icon.
Changing the font: Select a font from the toolbar.
 |
| Photo by IvanWalsh via flickr |
Thursday, 19 May 2016
WHAT'S THE INTERNET?
WHAT'S THE INTERNET USED FOR?
Communication: email, chat rooms, social networks and video-conferencing.
Sharing information: text, images, maps...
Playing games: online and downloadable games.
Banking and shopping.
HOW TO USE THE INTERNET:
What do you need to connect to the Internet? A telephone line, a router, an Internet service provider (ISP), a web browser.
What's a browser? A browser is a computer program that we use to connect to the Internet: Internet Explorer, Chrome, Firefox...
What's a router? A router sends and receives data. By connecting a computer to a router, it can send and receive information from the Internet.
 |
| Router, By Evan-Amos (Own work) [Public domain], via Wikimedia Commons |
What's an ISP? An ISP is a company that provides access to the Internet (Movistar, Vodafone, Orange...)
WHAT'S THE BEST WAY TO SEARCH FOR INFORMATION ON THE INTERNET?
The Internet has a huge amount of information on many different topics. The best way to find information is to use a search engine (Google, bing, kiddle, bunis...). You introduce a keyword and the search engine gives you a list of links: words or images that take you to web pages with information pages, shopping pages, photos...
HOW DO COMPUTERS WORK?
HISTORY OF COMPUTERS: The first computer was invented in 1943. It was used to break the codes used by the German army to send messages during World War II. It's name was Colossus because it occupied a whole room.
 |
| Ian Petticrew [CC BY-SA 2.0 (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/2.0)], via Wikimedia Commons |
 |
| By Jamo spingal (Own work) [CC BY 3.0 (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0)], via Wikimedia Commons |
 |
| IBM PC 515, By Ruben de Rijcke (Own work) [CC BY-SA 3.0 (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/3.0)], via Wikimedia Commons |
TYPES OF COMPUTERS:
General purpose machines: they can perform many functions: mobile phones...
Special purpose machines: they perform one specific function: GPS...
HOW HAVE INVENTIONS CHANGED ART AND MUSIC?
_@_The_Cutting_Room_Recording_Studios,_NYC.jpg/640px-SSL_SL9000J_(72ch)_@_The_Cutting_Room_Recording_Studios,_NYC.jpg) |
|
By Rebecca
Wilson (originally posted to Flickr as Vicariously) [CC BY 2.0
(http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/2.0)], via Wikimedia Commons
|
Other artists use modern software and technology to produce digital images. They use stylus and touch-sensitive pads to draw or to edit digital images.
 |
| Photo via youtube |
There are many inventions to help us doing exercise: running machines, exercise bikes, rowing machines, heart rate monitors...
 |
| By Tomwsulcer (Own work) [CC0], via Wikimedia Commons |
Thursday, 5 May 2016
MODELO DE EXAMEN DEL TEMA 14
Y aquí os dejo las soluciones:
ÁREA Y VOLUMEN DE UN PRISMA
aquí os dejo esta imagen que explica como se calcula el área de un prisma y también el volumen.
WHAT INVENTIONS DO WE USE IN OUR DAILY LIVES?
Modern machines have changed the way we live in many ways:
- Food production: machines have changed the way the food is prepared in large factories, sometimes it has been frozen or packaged in a tin, so it stays fresh for longer periods of time.
- Clothing: most of our clothes contain synthetic fabrics (nylon, viscose). So they're cheaper, more resistant to temperature than natural fabrics and they do not wear out so quickly.
- Healthcare: Doctors use microscopes, computers, X-ray machines and scanners...
By Cmglee (Own work) [CC BY-SA 3.0 (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/3.0) or GFDL (http://www.gnu.org/copyleft/fdl.html)], via Wikimedia Commons
The bicycle, cars (before the invention of cars we travelled by horse and carriage), steam engine, the hovercraft, aeroplanes...
Thursday, 28 April 2016
WHAT ARE PUBLIC SERVICES?
Taxes are deducted from workers' salaries and profits that companies make. We pay an extra tax every time we buy something or use a service. This is sales tax or value added tax.
The government collects taxes. These taxes are spent on public services such as schools, hospitals, libraries, street cleaning, building roads and providing for people's pensions when they retire.
 |
| Hospitals are part of public services. Photo by Francis Tyers via wikipedia |
Thursday, 21 April 2016
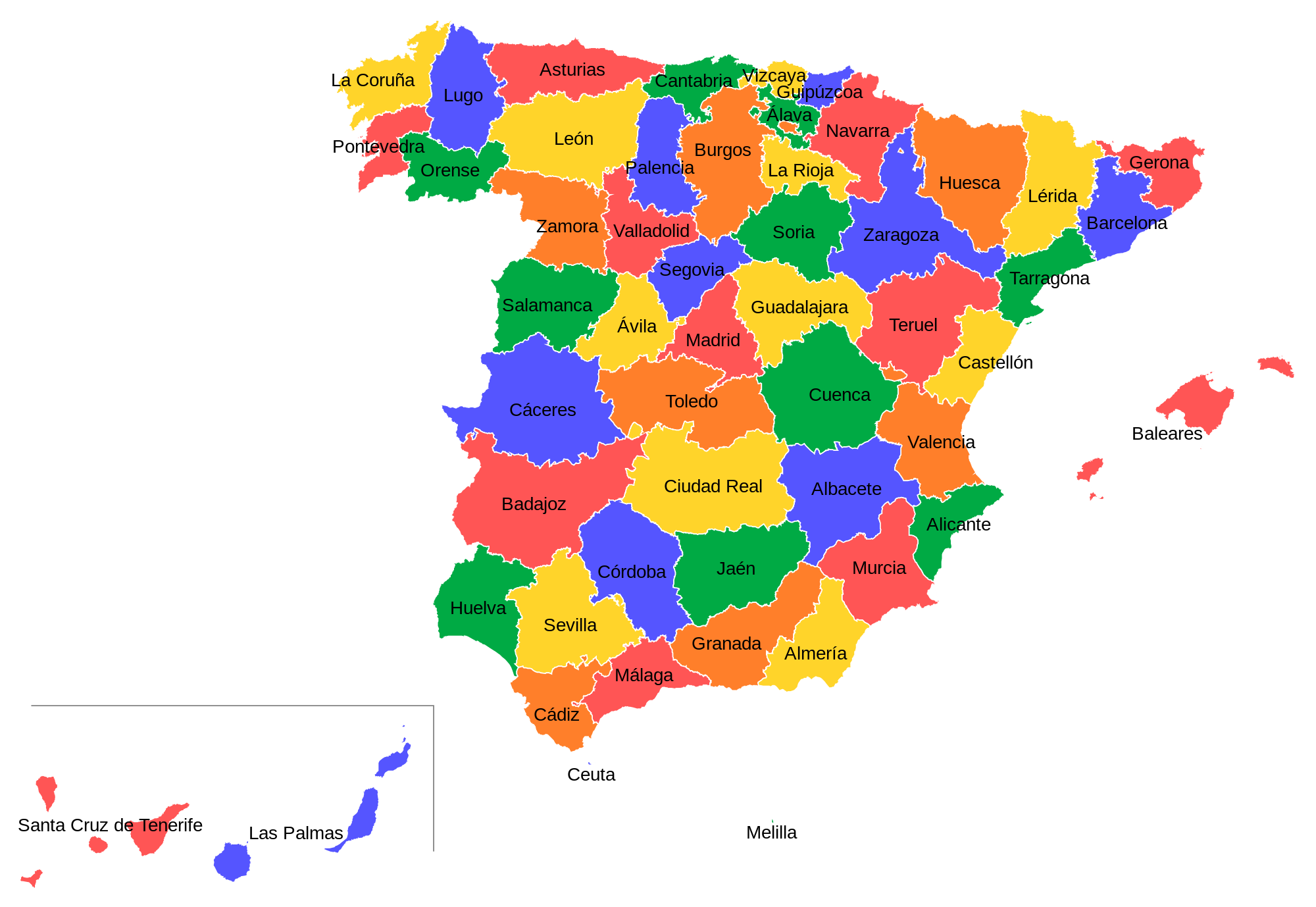
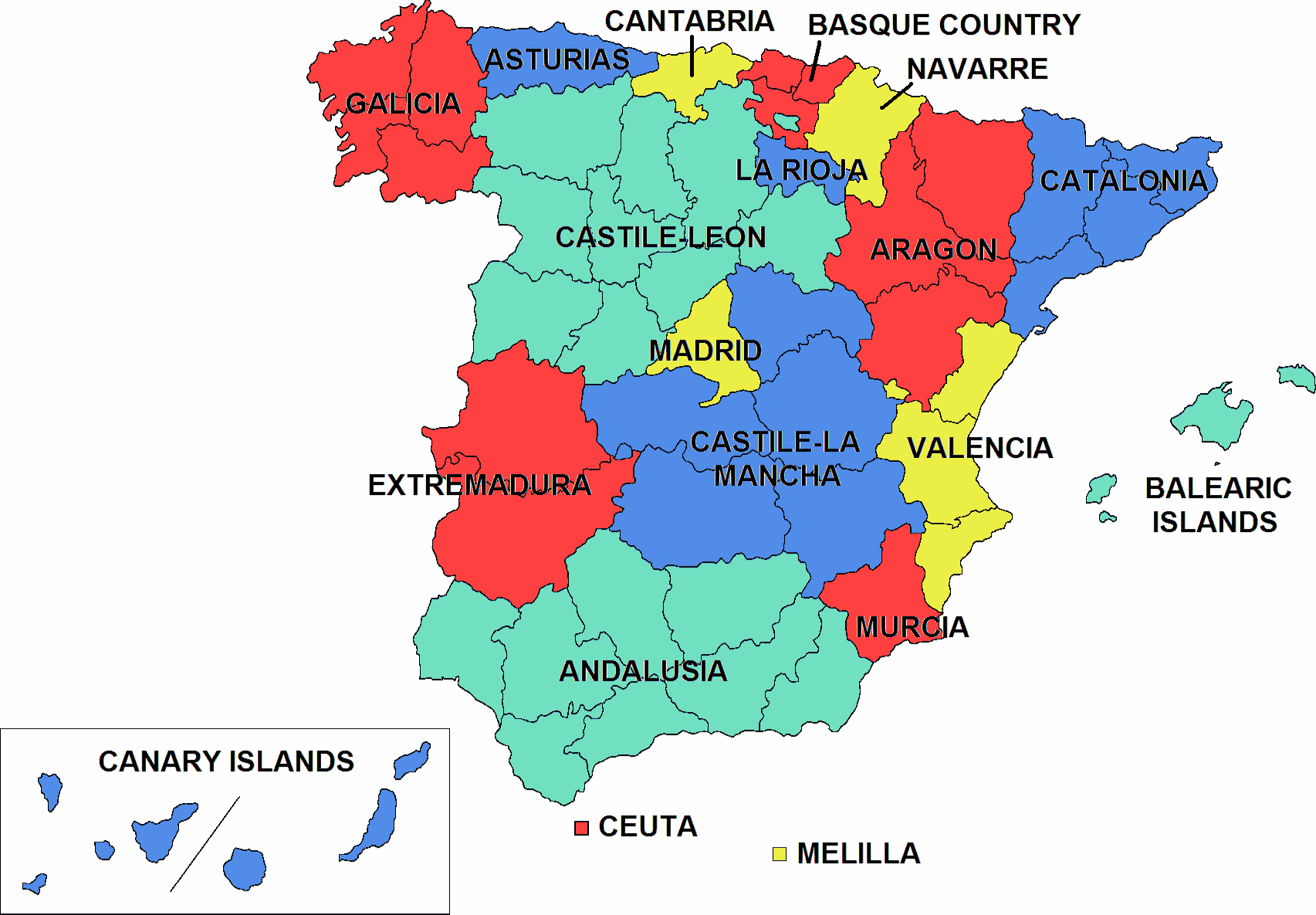
HOW IS SPAIN ORGANISED?
There are 50 provinces.
Each autonomous community has its own Statute of Autonomy. The Statute of Autonomy defines:
- The territory of each autonomous community.
- The governmental institutions.
- Its official language(s), flag, coat of arms and anthem.
- A regional parliament, which has legislative powers.
- A government, which has executive powers.
- A Superior Court of Justice, which has judicial powers.
 |
| Photo from wikipedia. |
MODELO DE EXAMEN DEL TEMA 13
aquí os dejo un modelo del examen del tema 13. Al final del examen están los ejercicios corregidos, aunque ya los hemos hecho en clase.
HOW IS POWER DISTRIBUTED IN SPAIN?
The Constitution established the division of powers: legislative, executive and judicial. each power is controlled by only one institution, so they're independent.
Legislative power is exercised by the Parliament (Cortes Generales).
Parliament makes the laws, approves the state budget and monitors the activity of the government.
It's made up of two parts: the lower house, or Congress (Congreso de los Diputados) and the upper house, or Senate (el Senado).
_14.jpg) |
| The Spanish Congress. Photo by Luis Javier Modino Martínez [CC BY 2.0 (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/2.0)], via Wikimedia Commons |
 |
| The Spanish Senate. By Lcsrns (Own work) [CC BY-SA 3.0 (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/3.0)], via Wikimedia Commons |
Deputies and Senators are elected by citizens in general elections every four years.
Executive power is exercised by the government. The government is composed of its leader, the president, and the ministers. The ministers are responsible for specific areas such as economy, education, health or industry. The government headquarters is Moncloa Palace.
Tuesday, 19 April 2016
WHAT'S A DEMOCRACY?
The United Nations Universal Declaration of Human Rights establishes fundamental human rights for all.
 |
| Eleanor Roosevelt and United Nations Universal Declaration of Human Rights in Spanish text. See page for author [Public domain], via Wikimedia Commons |
Rights in democracy (freedom to do something):
- The right to an education.
- The right to food and shelter.
- The freedom to live and travel wherever we choose.
- The freedom to express our opinions.
- The right to associate with others.
- The right to be treated equally by the law.
- we must obey the law.
- We must pay taxes to support public services.
- We must not tolerate discrimination because of religion or race.
- We should look after our environment.
- We should look after people who are weaker than us.
- We should be kind to animals.
- Voting.
Tuesday, 12 April 2016
HOW ARE ELECTROMAGNETS USED?
ELECTRIC BELL
When the circuit is closed and the current flows through the circuit, it produces a magnetic field in the electromagnet. The hammer is attracted to the elctromagnet and hits the bell. The movement of the hammer breaks the circuit and the hammer returns to its original position. Then the cycle begins again.
MAGLEV
A magnetic levitation train uses electromagnets to levitate above its track.
The maglev has electromagnets in the base of the train.
The tracks have magnets which repel the electromagnets in the train.
The magnets above and in front of the train attract the magnets in the train, causing the train to move forward.
SPEAKERS AND MICROPHONES
Electric current travels through the coil of wire. This creates a magnetic field that switches on and off rapidly.
The magnetic field attracts the magnet, which is attached to the cone.
The cone vibrates rapidly, producing sound waves.
WHAT ARE THE EFFECTS OF ELECTRICITY?
The electric current produces a little thermal energy as it travels through a wire, but it produces a lot of thermal energy travelling through other substances (in an oven...).
| A toaster uses thermal energy from electricity. Nick carson at en.wikipedia [CC BY 3.0 (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0)], via Wikimedia Commons |
Electrolysis is a chemical reaction produced when an electric current flows through a liquid solution of charged particles. We use elctrolysis in electroplating: coating a metal object with a thin layer of another metal.
WHAT'S THE EARTH'S MAGNETIC FIELD LIKE?
 |
| Magnetosphere. By NASA (http://sec.gsfc.nasa.gov/popscise.jpg) [Public domain], via Wikimedia Commons |
WHAT CAUSES THE MAGNETOSPHERE?
The centre of the Earth is made of liquid iron. This liquid moves slowly as the Earth rotates causing a magnetic field to form around the whole planet.
USING A COMPASS
A compass has a magnetised steel needle that is balanced inside a container. The north pole of the needle is painted red. It is attracted to the south pole of the magnetosphere: the magnetic north pole of the Earth. It will always point north.
 |
| Compass. By Evan-Amos (Own work) [Public domain], via Wikimedia Commons |
WHY IS THE MAGNETOSPHERE IMPORTANT?
It deflects solar radiation from the Sun back into space. Radiation is harmful for plant and animal life on Earth.
It also helps us to navigate using a compass.
WHAT'S A BAR MAGNET?
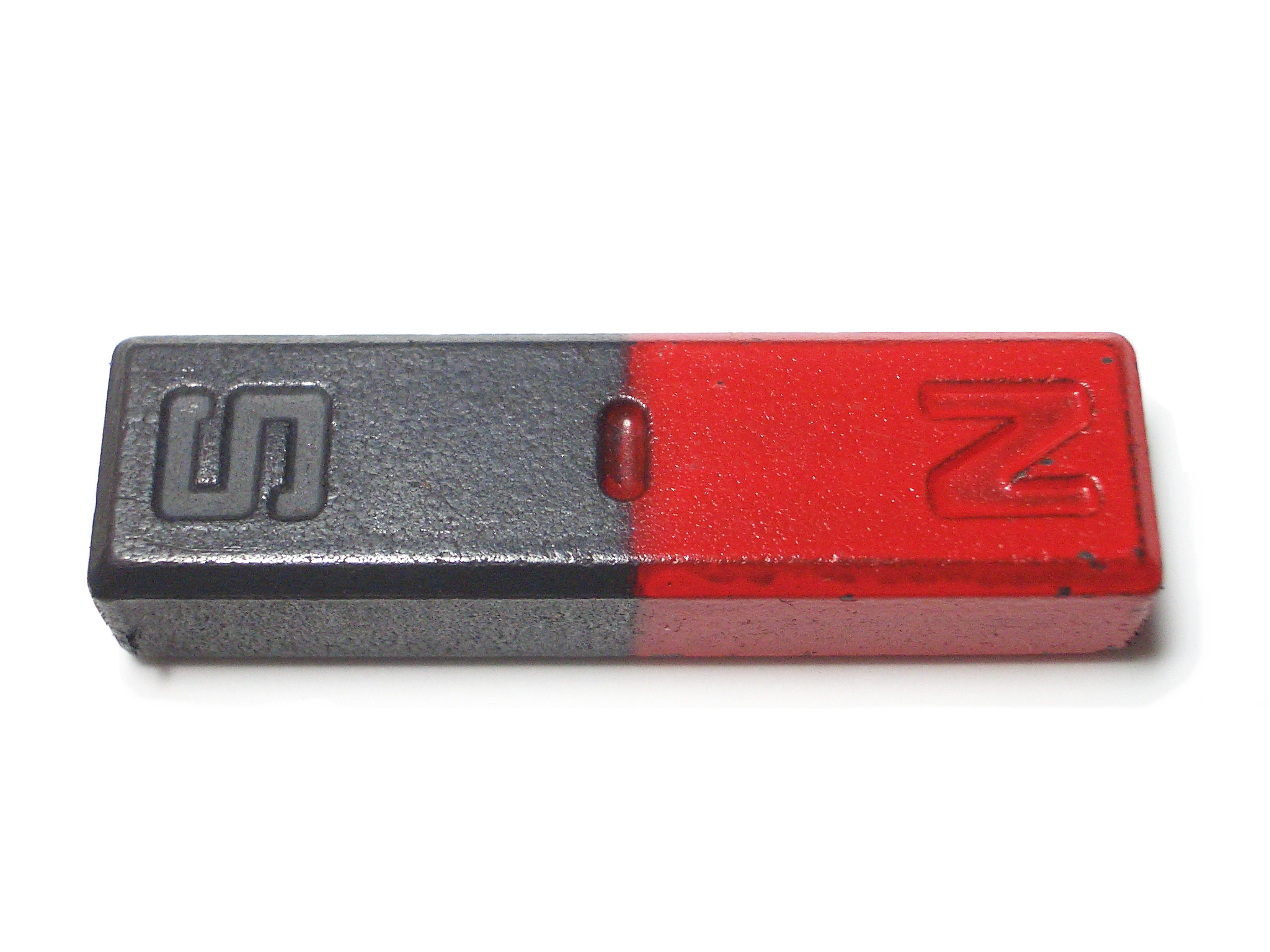 |
| Bar magnet. Photo taken by Aney, 2006-03-12, GFDL via Wikimedia |
WHAT DOES A MAGNETIC FIELD LOOK LIKE?
We can see the magnetic field of a bar magnet using iron filings.
 |
| By Alexander Wilmer Duff [Public domain], via Wikimedia Commons |
HOW DO WE REPRESENT MAGNETIC FIELDS?
We draw lines from the north pole to the south pole of the magnet. There are more lines and they're closer together near the poles because the magnetic field is stronger there.
WHAT HAPPENS WHEN TWO MAGNETS ATTRACT OR REPEL EACH OTHER?
Look at the pictures:
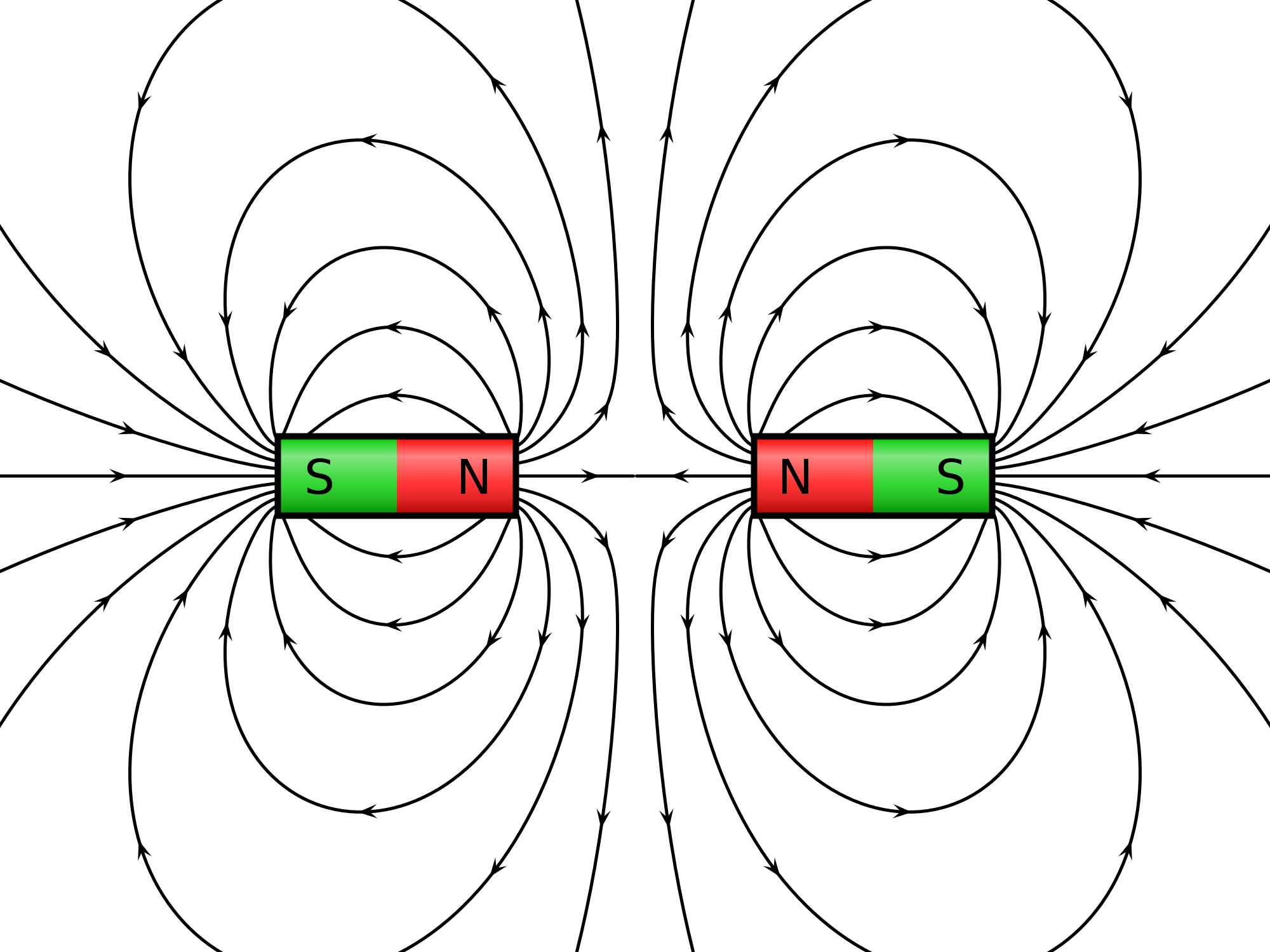 |
| Two magnets repelling. By Geek3 [GFDL (http://www.gnu.org/copyleft/fdl.html) or CC BY-SA 3.0 (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/3.0)], via Wikimedia Commons |
 |
| Two magnets attracting. By Geek3 [GFDL (http://www.gnu.org/copyleft/fdl.html) or CC BY-SA 3.0 (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/3.0)], via Wikimedia Commons |
HOW CAN WE IDENTIFY A MAGNET?
Magnets repel other magnets, but they don´t repel other substances.
HOW WAS ELECTROMAGNETISM DISCOVERED?
 |
| Picture from wikimedia |
André-Marie Ampere decided to study that phenomenon. He discovered the electron, which produces both, electricity and magnetism. But he named it the 'electrodynamic molecule'. Later, other scientists named it the electron.
 |
| By Ambrose Tardieu [Public domain], via Wikimedia Commons |
Michael Faraday discovered that by moving a loop of wire over a magnet, an electric current was produced in the wire. He invented the 'electromagnetic rotary device', the basis for the first electric motor or dynamo.
 |
| By Probably albumen carte-de-visite by John Watkins [Public domain], via Wikimedia Commons |
 |
| Faraday Disk Generator. By Émile Alglave [Public domain], via Wikimedia Commons |
SEPARATING MIXTURES WITH MAGNETS
Electromagnets are made from a wire coiled around an iron rod. The wire is connected to a power source. When the electric current flows along the wire a magnetic field is generated. When you stop the circuit, the electromagnet is switched off. Electromagnets are used in recycling plants to separate iron and steel from plastic, glass or other metals.